How they are formed?

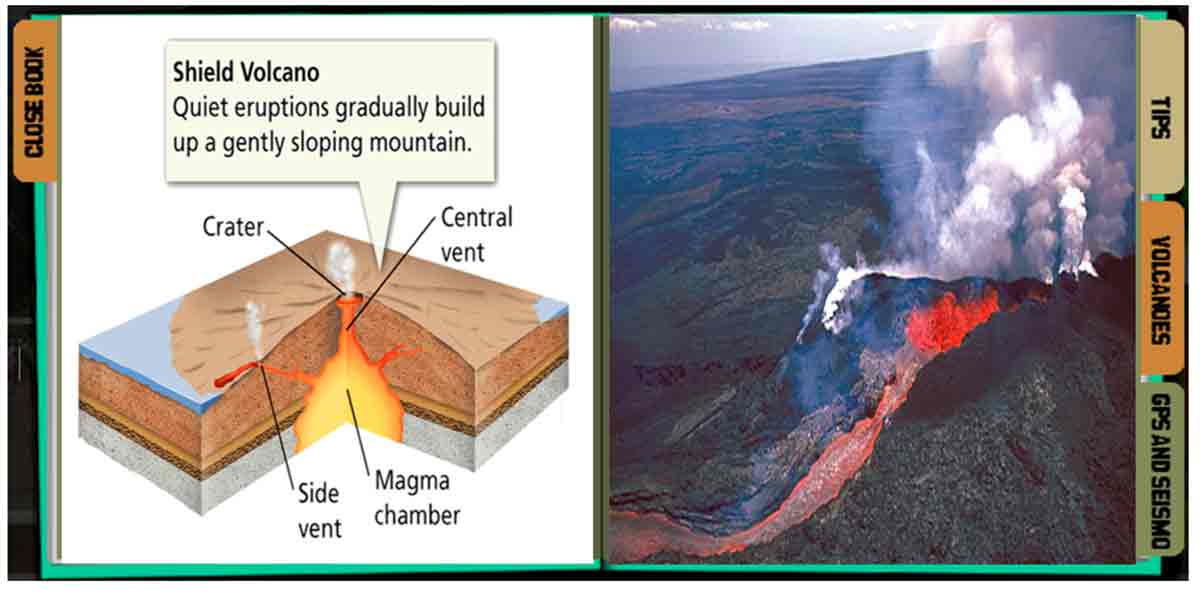
1. Shield volcanoes are formed by the accumulation of lava that oozes out from the volcano. Since non-viscous lava can flow freely, a broad, slightly domed structure that resembles a warrior’s shield is formed as shown .An example of this type is the Mauna Loa in Hawaii.
2. Cinder cones, on the other hand, are built from ejected lava fragments. They have a steep slope, wide crater and are the most abundant of the three major volcano types. One example of this type is the Paricutin in Mexico.

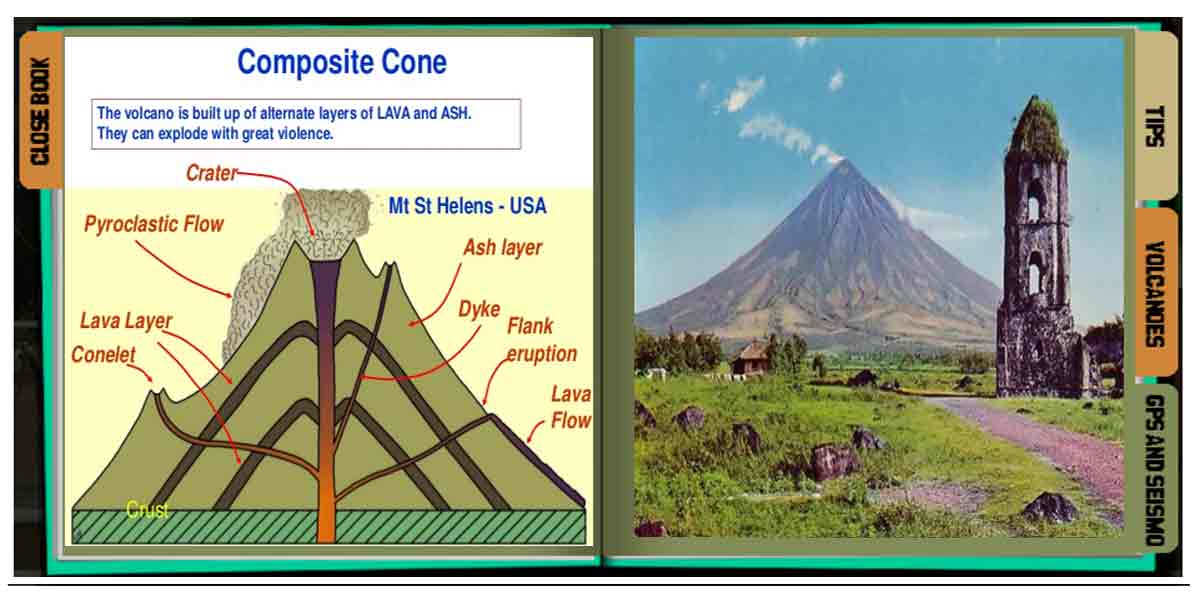
3. Composite cones or stratovolcanoes are large, nearly perfect sloped structure formed from alternate solidification of both lava and pyroclastic deposits. They can explode with great violence. One perfect example of this type of cone is our Mayon Volcano.